Manual Extraction: A Comprehensive Overview
Manual extraction encompasses retrieving data or materials by hand, without automation; it’s a foundational process evolving alongside technological advancements, impacting various fields.
What is Manual Extraction?
Manual extraction is fundamentally the process of retrieving data or physical materials from a source using human effort, eschewing automated tools or software. This involves a person directly accessing information from databases, documents, or physical samples. It’s a time-consuming, yet often necessary, method when dealing with unstructured data or situations where automated solutions are impractical or unavailable.
Essentially, it’s a hands-on approach, requiring careful observation and meticulous recording. While often viewed as less efficient than automated methods, manual extraction offers a level of nuance and adaptability that machines currently lack, particularly when dealing with complex or ambiguous information. It remains a cornerstone in many industries, despite the rise of automation.
The History of Manual Extraction Techniques
Historically, manual extraction predates the digital age by centuries. Early forms involved physically sifting through materials – think mining for ores or herbalists isolating compounds from plants. The advent of paper records necessitated manual data entry and collation, a laborious process forming the basis of early information management.

With the rise of databases, manual extraction shifted towards copying data from physical documents into digital formats. This remained prevalent until the late 20th century. Even today, despite sophisticated automation, manual techniques persist where legacy systems or unstructured data prevent automated solutions. The evolution reflects a constant interplay between human capability and technological advancement, continually refining extraction processes.
Manual Data Extraction: Processes and Challenges
Manual data extraction involves human retrieval of information from sources, a time-consuming process prone to errors, yet crucial for unstructured data handling.
Defining Manual Data Extraction
Manual data extraction is fundamentally the process of retrieving data from various sources – documents, databases, images – without the aid of automated tools or software. It relies entirely on human effort, involving individuals meticulously identifying and copying information. This differs significantly from automated methods utilizing Optical Character Recognition (OCR), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), or specialized extraction software.
Essentially, it’s a hands-on approach where data is manually inputted or transcribed. While often slower and more resource-intensive, manual extraction remains vital when dealing with complex, unstructured data formats where automated systems struggle with accuracy. It’s a foundational technique, particularly relevant when dealing with legacy systems or unique data structures.
The Steps Involved in Manual Data Extraction
Manual data extraction typically follows a structured, albeit labor-intensive, process. It begins with identifying the data sources – physical documents, digital files, or databases. Next, individuals carefully review these sources, locating the specific data points required. This is followed by the meticulous copying or transcription of the identified data into a designated format, such as a spreadsheet or database.
Data validation is a crucial step, ensuring accuracy and consistency. Finally, the extracted data undergoes quality checks to minimize errors. This entire process, while straightforward in concept, demands significant time and attention to detail, making it prone to human error if not carefully managed.
Common Challenges in Manual Data Extraction
Manual data extraction faces several inherent challenges. The most prominent is its time-consuming nature, especially with large volumes of data. Human error is a significant concern, stemming from fatigue, misinterpretation, or simple oversight during the copying process. Data inconsistencies can arise due to varying formats or subjective interpretations.
Scalability is another hurdle; expanding manual extraction efforts requires proportionally increasing personnel. Maintaining data security and compliance can also be difficult without automated controls. Ultimately, these challenges highlight the need for careful planning, robust quality control, and consideration of automation alternatives where feasible.
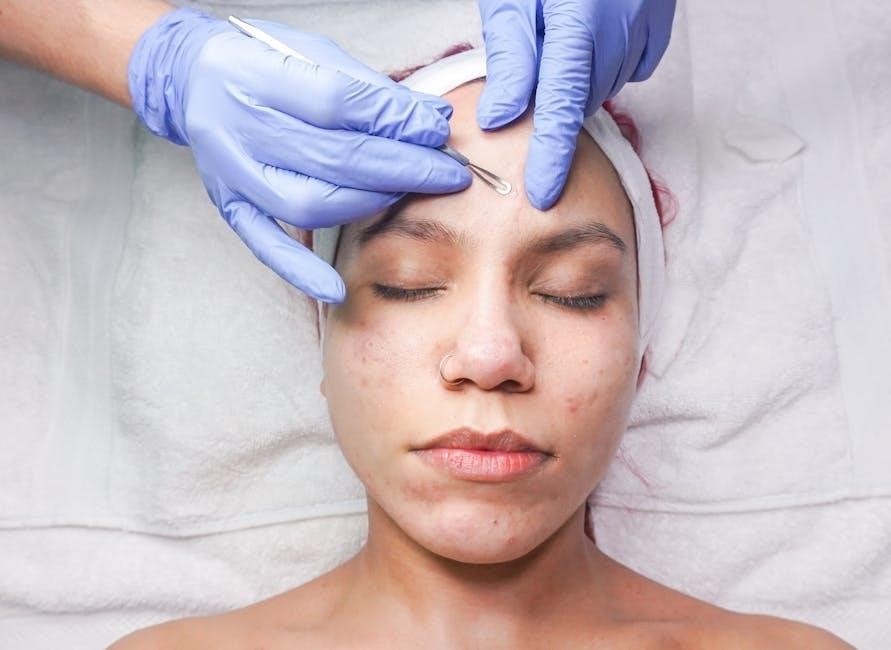
Manual Hair Extraction: A Surgical Technique
Manual Hair Extraction is a precise surgical method where follicular units are individually removed by hand, offering surgeons complete control.
The Precision of Manual Hair Extraction
Manual hair extraction distinguishes itself through exceptional precision, a cornerstone of successful hair restoration. Unlike automated techniques, this method allows surgeons to meticulously harvest each follicular unit individually, ensuring optimal graft quality and viability. This careful, hands-on approach grants complete control over the angle, direction, and depth of extraction, minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
The surgeon’s skill directly translates into a lower risk of damaging grafts, preserving their natural growth potential. This heightened precision is particularly crucial when dealing with delicate hair types or challenging donor areas. Ultimately, the meticulous nature of manual extraction contributes to denser, more natural-looking results, and improved patient satisfaction.
Advantages of Manual Hair Extraction
Manual hair extraction presents several key advantages for both surgeons and patients. The primary benefit lies in the enhanced control it offers, leading to superior graft quality and reduced follicular damage compared to automated methods. This translates to higher graft survival rates and more natural-looking results.
Furthermore, manual extraction is often preferred for patients with delicate scalp conditions or limited donor hair, as it minimizes trauma. It allows for selective harvesting, targeting the strongest, healthiest follicles. While potentially more time-consuming, the precision and improved outcomes often outweigh this consideration, making it a valuable technique in hair restoration surgery.
Comparing Manual vs. Automated Hair Extraction
Manual hair extraction, often referred to as Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), contrasts sharply with automated methods like robotic FUE. Manual techniques prioritize surgeon control and precision, allowing for selective graft harvesting and minimizing damage to surrounding tissue. Automated systems offer speed and potentially larger harvest numbers, but can sometimes compromise graft quality.
The choice between the two depends on individual patient needs and surgeon expertise. Manual extraction excels in cases requiring delicate precision or limited donor hair. Automated systems are suitable for larger sessions where speed is a priority. Ultimately, both aim for successful hair restoration, but differ in approach and potential outcomes.
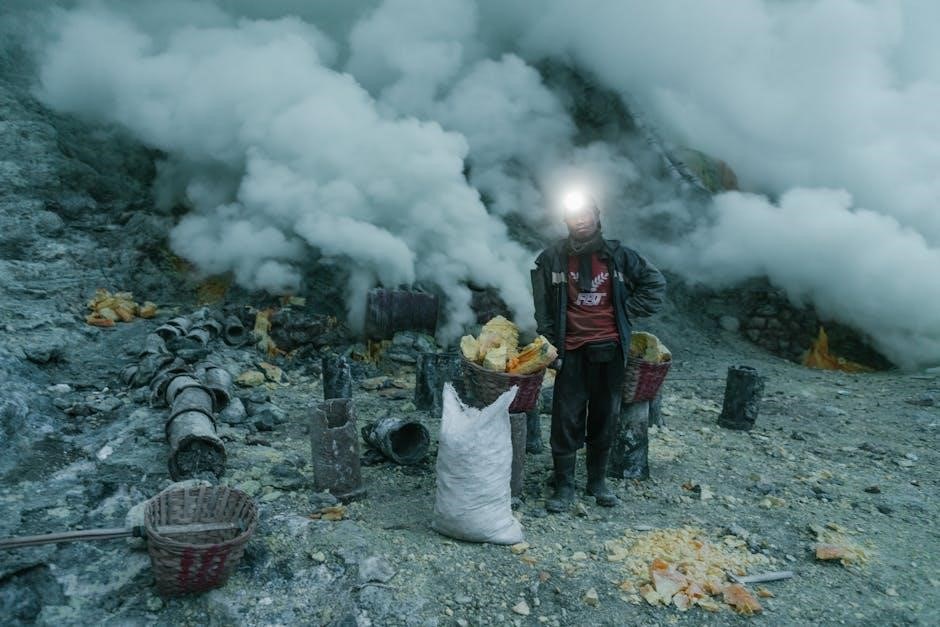

Extraction Techniques for Bioactive Compounds
Extraction techniques have significantly evolved, addressing challenges in recovering valuable bioactive compounds from natural sources, impacting both industry and environmental practices.
Traditional Extraction Methods
Historically, manual extraction relied heavily on time-honored techniques, often involving physical separation and solvent-based processes. These methods, while labor-intensive, formed the bedrock of obtaining desired compounds. Early approaches included simple maceration – soaking materials in a solvent – and percolation, where the solvent slowly passes through the sample.
These techniques demanded significant human effort for tasks like grinding, mixing, and filtering. The efficiency was limited, and consistency could be a challenge. However, they represented the initial steps in isolating bioactive compounds from natural matrices, paving the way for more sophisticated methodologies. These foundational methods continue to inform modern extraction strategies, even with advancements in automation.
Soxhlet Extraction: Principles and Applications
Soxhlet extraction, though utilizing specialized apparatus, often involves a degree of manual oversight and preparation. This continuous extraction technique relies on repeatedly cycling a solvent through the sample. The process begins with manually preparing the sample and loading it into the thimble.
As the solvent boils, its vapors rise and condense, dripping onto the sample, extracting desired compounds. Once the solvent level reaches a certain point, it siphons back into the flask, carrying the extracted material. This cycle continues, maximizing extraction efficiency. While automated versions exist, initial setup, monitoring, and solvent recovery often require manual intervention, making it a blend of technique and hands-on operation.
Modern Advancements in Extraction Techniques
Despite advancements, the need for manual extraction persists in specific scenarios, often as a crucial step before employing automated systems. While technologies like supercritical fluid extraction and ultrasound-assisted extraction offer efficiency, initial sample preparation – grinding, weighing, and loading – frequently demands manual labor.
Furthermore, certain specialized extractions, particularly those involving delicate compounds or small sample sizes, benefit from the precision only a skilled technician can provide. Modern techniques often reduce the extent of purely manual work, but rarely eliminate it entirely, highlighting the continued relevance of human expertise alongside technological progress.
Cannabis Extracts: A Focus on Butane Hash Oil (BHO)
Manual processes are integral to BHO production, involving careful handling of plant material and monitoring the extraction process for optimal yield and quality.
Understanding Butane Hash Oil (BHO)

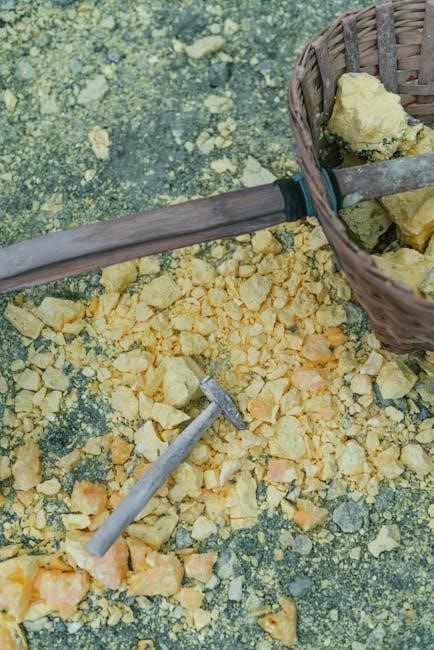
Butane Hash Oil (BHO), often called butane honey oil, represents a concentrated cannabis extract prized for its potency. While modern systems exist, initial BHO production heavily relied on manual techniques. Skilled operators meticulously controlled the flow of butane through cannabis plant material, observing color changes and viscosity to gauge extraction progress.
This manual observation was crucial, as over-extraction could lead to unwanted compounds being dissolved, impacting purity. Post-extraction, purging residual butane often involved manual monitoring of vacuum ovens, adjusting heat and pressure based on visual cues. The entire process demanded significant expertise and a delicate touch, highlighting the role of human skill in early BHO creation. Even today, quality control often includes manual inspection of the final product;
The Extraction Process for BHO

The BHO extraction process, even with modern equipment, often retains elements of manual control. Initially, cannabis plant material is packed into a glass or stainless steel column. Butane is then passed through this column – a process that, historically, was entirely manually regulated by controlling valve timings and observing solvent flow.
Following extraction, the resulting mixture, known as crude, undergoes purging to remove residual butane. This often involves manual adjustments to vacuum oven settings, monitoring temperature and pressure to optimize solvent removal without degrading the extract. Skilled operators visually assess the bubbling process, a manual indicator of remaining butane. Finally, collection and handling of the BHO itself frequently require manual dexterity and precision.
Safety Considerations in BHO Extraction

Manual aspects of BHO extraction inherently elevate safety concerns. Butane is highly flammable, demanding meticulous attention to ventilation and eliminating ignition sources – a manual vigilance crucial throughout the entire process. Historically, manual control of solvent flow increased the risk of leaks and uncontrolled releases.
Even with closed-loop systems, manual purging requires careful monitoring to prevent solvent buildup and potential explosions. Operators must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), a manual step often overlooked. Furthermore, manual handling of the finished BHO necessitates caution to avoid contamination and ensure proper storage. Thorough training and adherence to strict safety protocols are paramount when manual techniques are involved.
Data Extraction Methods: Classification-Based Techniques
Manual classification-based data extraction relies on human judgment to categorize and retrieve information, proving widely accepted and efficient for specific tasks.
Overview of Classification-Based Data Extraction
Classification-based data extraction, when performed manually, involves a human operator categorizing data points into predefined classes. This method is particularly useful when dealing with unstructured or semi-structured information where automated tools struggle; The process necessitates a deep understanding of the data and the classification criteria.
Unlike automated systems, manual classification allows for nuanced interpretation and handling of ambiguous cases. Operators can leverage contextual understanding and domain expertise to ensure accuracy. However, it’s inherently time-consuming and prone to human error, especially with large datasets. Despite these drawbacks, its simplicity and adaptability make it a valuable technique in specific scenarios, offering a balance between precision and resource investment.
Efficiency and Ease of Use
Manual data extraction, while straightforward in concept, often lacks efficiency, particularly when handling substantial volumes of information. It’s a time-intensive process, relying heavily on human effort and concentration. The ease of use stems from its minimal technological requirements – primarily, a human operator and the source data. However, this simplicity comes at the cost of scalability and speed.
Compared to automated methods, manual extraction is significantly slower and more susceptible to errors. The repetitive nature of the task can lead to fatigue and decreased accuracy. While no specialized software is needed initially, the overall process can become cumbersome and costly due to the labor involved, making it less practical for large-scale projects.
Applications of Classification-Based Methods
Although seemingly counterintuitive to “manual” extraction, classification-based techniques can assist in streamlining the process. These methods involve pre-defining categories or classes within the data, allowing a human operator to more quickly and consistently identify and extract relevant information. This is particularly useful when dealing with structured or semi-structured data sources.
For example, in document processing, classifying documents by type (invoice, contract, report) before manual review speeds up extraction. This approach reduces cognitive load and minimizes errors. While not fully automated, it enhances the efficiency of manual efforts, making it a practical solution for tasks where full automation isn’t feasible or cost-effective.

Finding Manuals Online
Lost manuals are easily replaced! Online libraries offer a vast collection of original user guides from manufacturers, simplifying access to crucial information.
Online Libraries of User Manuals
Numerous online repositories specialize in archiving and distributing user manuals, offering a convenient solution for locating documentation for a wide array of products. These digital libraries frequently categorize manuals by brand, model number, or product type, facilitating efficient searches.

Search functionalities typically allow users to input keywords, manual names, or specific product details to narrow down results. Listings often include details such as manual size, page count, and a brief description to aid in identification.
Many platforms provide options to view manuals directly online or download them as PDF files for offline access, ensuring accessibility and convenience for users needing guidance or troubleshooting assistance.
Locating Specific Manuals
Successfully finding a particular manual often begins with precise keyword searches within online libraries. Utilizing the product’s model number is highly recommended, as it significantly refines search results. If the model number is unknown, detailed descriptions of the product’s features or manufacturer can prove helpful.
Exploring manufacturer websites directly is another effective strategy, as many companies maintain archives of their product documentation. Additionally, specialized forums or online communities dedicated to specific products can offer valuable leads or direct links to relevant manuals.
Remember to try variations of search terms and consider potential misspellings to broaden the search scope and increase the likelihood of locating the desired documentation.
Benefits of Accessing Online Manuals
Accessing manuals online offers numerous advantages over traditional paper copies. Immediate availability is a key benefit – no waiting for shipping or searching through physical archives. Online manuals are often searchable, allowing users to quickly locate specific information or troubleshooting steps.
Furthermore, digital formats reduce environmental impact by minimizing paper consumption. Online resources are frequently updated, ensuring access to the most current information and revisions. The convenience of accessing manuals from any device with an internet connection enhances usability.
Cost savings are also significant, as accessing online manuals is typically free of charge, eliminating purchase costs.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.